
What is a sponge city?
The construction of the sponge city is regarded as an important measure to enhance the city’s flood control capacity. Its practice is to effectively control the rainwater absorption, storage and slow release of rainwater through infrastructure, roads and green space through strengthening urban planning and management. run-off. The construction of the sponge city is a large-scale system engineering. The United States has a long history and rich experience in the management of water resources. As early as 1899, the United States enacted the “Refuse Act of 1899”, stipulating that no waste waste should be put into the water body except with the permission of the Army Department. After the promulgation of the federal Clean Water Act (CWA) in 1972, the permit review authority for designated water bodies was transferred to the Federal Environmental Protection Agency for the implementation of the Water Pollutant Discharge Permit System (NPDES) work. The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers continues to implement the review and issuance of the CWA 404 license and is responsible for the management of wetlands, rivers, lakes, offshore waters, etc. In the Clean Water Act, almost all water bodies (including surface runoff) are considered national assets and are called Waters of the United States. After half a century of careful management, the US water resources have become cleaner.
Sponge City is a metaphorical saying. It is a new urban model that builds flood control and flood control in the city and has ecological and environmental protection functions. For example, building a permeable pavement to replace a non-permeable pavement. The international terminology is “the construction of low-impact development rainwater system”. When it rains, it absorbs water, accumulates water, seeps water, cleans water, and releases and uses the stored water when needed to realize the free migration of rainwater in the city. “Sponge City” is an innovative performance that promotes the construction of green buildings, the development of low-carbon cities, and the formation of smart cities. It is an organic combination of modern green new technologies and various factors such as society, environment and humanities, and is the cornerstone of social progress. The material of “Sponge City” material is applied, showing excellent water seepage, compression resistance, wear resistance, anti-skid, environmental protection, beautiful and colorful, comfortable and easy to maintain, sound absorption and noise reduction, etc. It has become a “breathing” urban landscape pavement, and is also effective. It alleviates the urban heat island effect and makes the urban road no longer hot.
Sponge City has several characteristics
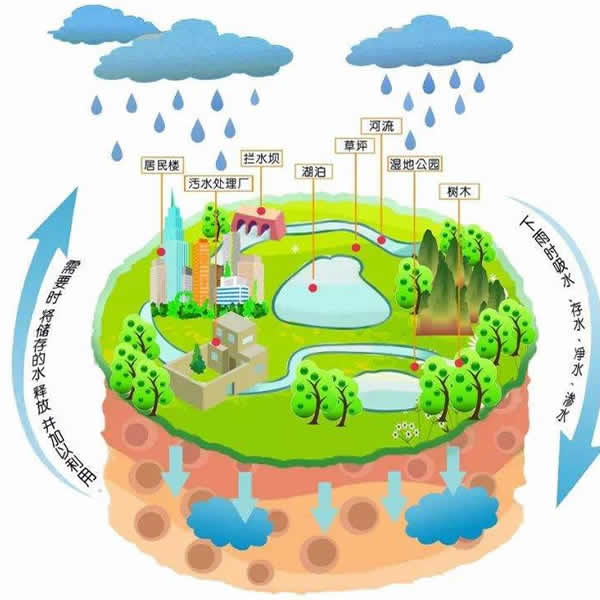
First, the rain on the sky is digested as much as possible. This is what is commonly referred to as water storage. There are surface water storage such as reservoirs and lakes. There are underground water storage such as permeable roads and groundwater.
Second, the flow of water from the local must be clear as a sweet spring. This is what is commonly referred to as sewage treatment. The sewage generated locally must be treated locally. The burden of treating sewage cannot be left to the downstream.
Third, local water storage on the surface and underground water storage must be used repeatedly and efficiently.
Fourth, each block of the sponge city should try to meet all local water needs.
Fifth, gradually improve the ecological environment function of the sponge city.
Sixth, the ideal goal of the sponge city is to build the sponge city into a new green mountain and green water, which makes the sponge city return to an integral part of the natural ecology.
Sponge City Construction Ideas

Construct a sponge city with “natural accumulation, natural penetration, and natural purification”. These three “nature” emphasize that the primary advantage of the sponge city is to collect and utilize the rainwater “turning waste into treasure” and emphasize the use of ecological methods to strengthen the city’s rainwater management capacity. More rains and less drainage, improve the utilization of rainwater, and minimize the impact on the ecological environment in urban development. It is the basic concept of sponge city construction. According to the provisional regulations for the preparation of special plans for sponge cities, it should be based on urban rainfall, soil, topography, etc. Factors and economic and social development conditions, comprehensive consideration of current status issues and construction needs in water resources, water environment, water ecology, water safety, etc., adhere to the combination of problem orientation and goal orientation, and adopt “infiltration, stagnation, storage, and net, according to local conditions. Use, row, and other measures.
The construction of the sponge city is reflected in the “transformation” of the four relatively traditional development methods: from “demand-based supply” to “supply-demand”; from “development intensity control” to “consideration of low-environment impact development” Construction intensity control”; from “end management” to “source reduction, process control, system governance, overall planning”; from “traditional fast-discharge mode” to “infiltration, stagnation, storage, net, use, platoon.” The six words “infiltration, stagnation, storage, net, use, and drainage” can be summarized as the technical elements of the construction of the sponge city.
US sustainable rainwater management experience
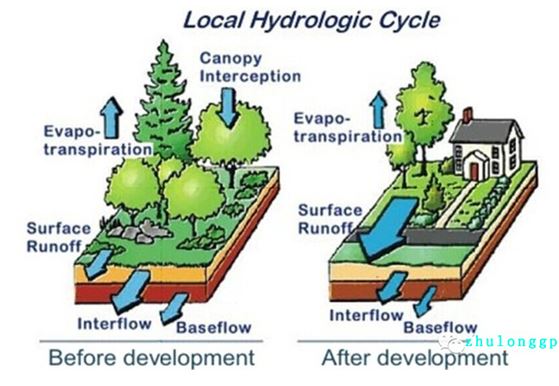
Clean water comes from unpolluted rainwater. Rainwater management in the United States began in the early 1990s. Although the federal Clean Water Act completed legislation in 1972, the US Environmental Protection Agency has not successfully introduced a method to manage rainwater due to the large scope of control and difficulties in monitoring, measuring, and managing rainwater. Based on this, water pollution caused by rainwater discharge has become the culprit of water quality deterioration in the United States.
After the revision of the Clean Water Act of 1987, at the urging of Congress, the US Environmental Protection Agency introduced a rainwater control scheme to incorporate rainwater emissions into the NPDES (National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System) control system, and stipulated that: 1 rainwater discharge Units (such as urban and rural areas and industrial areas) need to apply for NPDES licenses; 2 rainwater discharge units need to develop a Storm Water Pollution Prevention Plan (SWP3); 3 rainwater discharge units need to implement the best control measures proposed in SWP3 ( Best Management Practices (BMPs); 4 Rainwater discharge units need to be sampled to ensure the quality of the discharged rainwater meets the standards specified in the permit. So far, the United States reached the goal of “clean” discharge of rain in the late 1990s.
For a long time, the US Army Corps of Engineers has been responsible for protecting and managing water bodies such as wetlands, rivers, and lakes. Any action on the water body must first be approved by the Army Corps of Engineers CWA 404, in accordance with the provisions of the card. At the same time, the Army Corps of Engineers has the responsibility to perform the conservation, repair and restoration of water bodies. Under this management system, wetlands are protected or compensated. The surrounding areas of the water body are maintained and trimmed, and rivers and lakes are sustainably ecologically restored. In this way, the water resources of the United States can be further protected after being cleaned.
As the guardian of water resources, the US Army Corps of Engineers proposed the water management for environmental sustainability in 2002, emphasizing the importance of ecological balance and water conservation. The US Environmental Protection Agency also proposed a similar policy in 2010. Due to the emphasis on environmental sustainability, ecological balance has received widespread attention. Water storage has become the first priority of the Army Corps of Engineers. Natural water storage mechanisms (such as the water storage function of forest wetlands and the constant refilling of underground water reservoirs) have also been extensively explored. At this point, the US water management has once again been improved and improved, and the practice of saving after the clean conservation.
The meaning of the sponge city
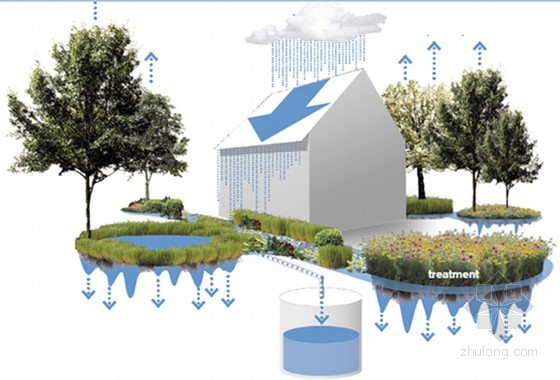
The essence of the construction of the sponge city is to create a sustainable rainwater management system, which is vital and rich in the positive significance of ecological civilization construction. Sustainable development is the basic national policy of the country and the cornerstone for maintaining national security and stability. Sponge City’s philosophy of ecologically balanced water management practices is a key element in ensuring sustainable development. We emphasize that the construction of sponge cities should aim at conserving water resources, and it is the primary task to promote the smooth return of surface runoff into the underground reservoir. Based on this, we will sort out the management system of sustainable rainwater, think about the scientific planning standards of sponge city, compare the experience of water resources management in the United States and China, and propose the problems that need to be paid attention to in the current construction of China’s sponge city, and seek a set of problems. Effective and available practices for domestic relevant units to refer to when planning sponge cities.
